The Arduino community has created a wide variety of modules, sensors, and other peripherals that you can use to easily create electronic projects. We have tutorials for the most popular components. This article is a compilation of 39 free guides for different sensors, modules, and peripherals compatible with Arduino boards.

Here’s a quick list of the sensors/modules divided into different categories:
- DHT11/DHT22 Humidity and Temperature Sensor
- DS18B20 Temperature Sensor
- LM35, LM335 and LM34 Temperature Sensors
- K-Type Thermocouple with MAX6675 Amplifier
- BMP180 Barometric Sensor
- BME280 Sensor with Arduino (Pressure, Temperature, Humidity)
- BME680 Environmental Sensor with Arduino (Gas, Temperature, Humidity, Pressure)
- BMP388 Altimeter with Arduino (Pressure, Altitude, Temperature)
- MQ-2 Gas/Smoke Sensor
- BH1750 Ambient Light Sensor
- TDS Sensor (Water Quality Sensor)
- FC-37 or YL-83 Rain Sensor
- YL-69 or HL-69 Soil Moisture Sensor
- PIR Motion Sensor
- HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor
- RCWL-0516 Microwave Radar Sensor
- Door Sensor (reed switch)
- Tilt Sensor
- MPU6050 Accelerometer and Gyroscope
- NEO-6M GPS Module
Other Sensors/Modules/Peripherals:
- DS1307 or DS3231 Real Time Clock (RTC)
- Microphone Sound Sensor
- Relay Module
- microSD Card Module
- Load Cell with HX711 Amplifier
- Fingerprint Sensor Module (FPM10A)
- TCS230/TCS3200 Color Sensor
- OLED Display
- 8×8 Dot Matrix
- LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)
- 1.8 TFT Display
- RGB LED
- Addressable RGB LED Strip WS2812B
- MFRC522 RFID Reader
- nRF24L01
- 433 MHz Transmitter/Receiver
- Infrared Receiver
- SIM900 GSM Shield
- Membrane Keypad
Environmental Sensors
1. DHT11/DHT22 Humidity and Temperature Sensor
The DHT11 and DHT22 sensors are used to measure temperature and relative humidity. These sensors contain a chip that does analog to digital conversion and spits out a digital signal with the temperature and humidity. This makes them very easy to use with any microcontroller.
To get started, follow the next tutorial:
Get a DHT22 temperature and humidity sensor.
Get a DHT11 temperature and humidity sensor.
2. DS18B20 Temperature Sensor
The DS18B20 temperature sensor is a one-wire digital temperature sensor. This means that it just requires one data line (and GND) to communicate with your Arduino board. Each DS18B20 temperature sensor has a unique 64-bit serial code. This allows you to wire multiple sensors to the same data wire. So, you can get temperature from multiple sensors using just one Pin.
The DS18B20 temperature sensor is also available in waterproof version.
Follow the next tutorial to get started with the DS18B20 temperature sensor and the Arduino:
Get a DS18B20 Temperature Sensor.
Get a DS18B20 Temperature Sensor (waterproof version).
3. LM35, LM335 and LM34 Temperature Sensors
The LM35, LM335, and LM34 are linear temperature sensors that output a voltage proportional to the temperature value. The LM35, LM335, and LM34 sensors work in a similar way, but are calibrated differently to output a voltage proportional to the different temperature units:
- LM35: proportional to temperature in Celsius (ºC)
- LM335: proportional to the temperature in Kelvin (ºK)
- LM34: proportional to the temperature in Fahrenheit (ºK)
Learn how to interface the LM35, LM335, and LM34 sensors with the Arduino board:
Get a LM35 Temperature Sensor.
Get a LM335 Temperature Sensor.
Get a LM34 Temperature Sensor.
4. K-Type Thermocouple with MAX6675 Amplifier
A K-type thermocouple is a type of temperature sensor with a wide measurement range like −200 to 1260ºC (−326 to 2300ºF). To get the temperature from the thermocouple we need a thermocouple amplifier. We use the MAX6675 amplifier that is sold together with the thermocouple, but you can use any other amplifier, like the MAX31855.
To get started, follow the next tutorial:
Get the Type-K Thermocouple temperature sensor.
5. BMP180 Barometric Sensor
The BMP180 is a digital pressure sensor and it measures the absolute pressure of the air around it. It features a measurement range from 300 to 1100hPa with an accuracy down to 0.02 hPa. Because temperature affects the pressure, the sensor comes with a temperature sensor to give temperature-compensated pressure readings.
Additionally, because the pressure changes with altitude, you can also estimate the altitude based on the current pressure measurement. The sensor communicates with the Arduino using I2C communication protocol.
To get started, follow the next tutorial:
Get a BMP180 barometric sensor.
6. BME280 Sensor with Arduino (Pressure, Temperature, Humidity)
The BME280 sensor module reads barometric pressure, temperature, and humidity. Because pressure changes with altitude, you can also estimate altitude. There are several versions of this sensor module: some can communicate using only I2C communication protocol, and others have the additional option to use the SPI communication protocol. We usually use the I2C protocol with this sensor. This sensor is very versatile and we use it in many of our tutorials.
To get started, follow the next tutorial:
Get a BME280 temperature, humidity, and pressure sensor.
7. BME680 Environmental Sensor with Arduino (Gas, Temperature, Humidity, Pressure)
The BME680 is an environmental sensor that combines gas, pressure, humidity, and temperature sensors. The gas sensor can detect a broad range of gases like volatile organic compounds (VOC). For this reason, the BME680 can be used in indoor air quality control.
Learn how to get started with the BME680 and the Arduino board:
Get a BME680 environmental sensor.
8. BMP388 Altimeter with Arduino (Pressure, Altitude, Temperature)
The BMP388 is a precise, low-power, low-noise absolute barometric pressure sensor that measures absolute pressure and temperature. Because pressure changes with altitude, we can also estimate altitude with great accuracy. For this reason, this sensor is handy for drone navigation and other applications like vertical velocity calculation; weather forecasts, and weather stations; health care applications; fitness applications; and much more.
To get started, follow the next tutorial:
Get a BMP388 altimeter sensor.
9. MQ-2 Gas/Smoke Sensor
The MQ-2 smoke sensor is sensitive to smoke and to the following flammable gases: LPG, Butane, Propane, Methane, Alcohol, and Hydrogen. The resistance of the sensor is different depending on the type of gas.
To get started, you can follow the next tutorial:
10. BH1750 Light Sensor
The BH1750 is a 16-bit ambient light sensor that communicates via I2C protocol. It outputs luminosity measurements in lux (SI-derived unit of illuminance). It can measure a minimum of 1 lux and a maximum of 65535 lux. It can be used in a wide variety of projects. For example: to detect if it is day or night; to adjust or turn on/off LED’s brightness accordingly to ambient light; to adjust LCDs and screen brightness; to detect if an LED is lit; etc.
To get started, follow the next tutorial:
Get a BH1750 ambient light sensor.
11. TDS Sensor (Total Dissolved Solids)
A TDS meter indicates the total dissolved solids like salts, minerals, and metals, in a solution. This parameter can be used to give you an idea of water quality and compare water from different sources. One of the main applications of a TDS meter is aquarium water quality monitoring.
To get started, follow the next tutorial:
Get a TDS (total dissolved solids) sensor.
12. FC-37 or YL-83 Rain Sensor
The rain sensor is used to detect water and it can detect beyond what a humidity sensor can. You can estimate the relative amount of water accordingly to the sensor’s resistance output.
Learn how to use the rain sensor with the Arduino using the following tutorial:
13. YL-69 or HL-69 Soil Moisture Sensor
The soil moisture sensor or the hygrometer is usually used to detect the humidity of the soil. So, it is perfect to build an automatic watering system or to monitor the soil moisture of your plants.
Get started with the soil moisture sensor with the Arduino:
Get a soil moisture sensor YL-69 or HL-69.
Motion-Related Sensors
14. PIR Motion Sensor
The PIR motion sensor is ideal to detect movement. PIR stands for “Passive Infrared” and it measures infrared light from objects in its field of view. So, it can detect motion based on changes in infrared light in the environment. It is ideal to detect if a human or animal has moved in or out of the sensor range.
Get started with the PIR motion sensor and Arduino:
Get a PIR Motion Sensor (HC-SR501).
15. HC-SR04 Ultrasonic Sensor
The HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor uses sonar to determine the distance to an object. This sensor reads from 2cm to 400cm (0.8inch to 157inch) with an accuracy of 0.3cm (0.1inches), which is good for most hobbyist projects. In addition, this particular module comes with ultrasonic transmitter and receiver modules.
Get started with one of the following tutorial:
Get an HC-SR04 ultrasonic sensor.
16. RCWL-0516 Microwave Radar Sensor
The RCWL-0516 is a small, inexpensive sensor that uses microwave radar to detect the presence of moving objects. The RCWL-0516 sensor has a single output pin that goes HIGH when it detects movement. It outputs LOW when no motion is detected. This sensor is many times used as an alternative to the PIR motion sensor.
Get started with the following tutorial:
Get an RCWL-0516 microwave radar sensor.
17. Door Sensor (reed switch)
A magnetic contact switch is a reed switch encased in a plastic shell so that you can easily apply it on a door, a window, or a drawer to detect if it is open or closed.
Get started with the following tutorial:
18. Tilt Sensor
The tilt sensor is many times referred to as inclinometer, tilt switch or rolling ball sensor. Using a tilt sensor is a simple way to detect orientation or inclination.
Get started with the tilt sensor and Arduino using the following tutorial:
Get a tilt sensor (inclinometer).
19. MPU6050 Accelerometer and Gyroscope
The MPU-6050 IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) is a 3-axis accelerometer and 3-axis gyroscope sensor. The accelerometer measures the gravitational acceleration and the gyroscope measures the rotational velocity. Additionally, this module also measures temperature. This sensor is ideal to determine the orientation of a moving object.
To get started, follow the next tutorial:
Get an MPU6050 accelerometer and gyroscope.
20. NEO-6M GPS Module
The NEO-6M GPS module is a compact and affordable device that provides accurate global positioning system (GPS) location information. When paired with an Arduino, it enables projects to incorporate precise location tracking and navigation capabilities.
Get started with the GPS module and Arduino using the following tutorial:
Other Sensors/Modules/Peripherals
21. DS1307 or DS3231 Real Time Clock (RTC)
The DS1307 and DS3231 are real-time clock modules used with Arduino. They allow you to track the time for tasks like scheduling and data logging.
Learn how to use the RTC module with the Arduino:
Get a Real Time Clock Module (DS1307).
22. Microphone Sound Sensor
The microphone sound sensor, as the name says, detects sound. It gives a measurement of how loud a sound is. The sensor outputs a HIGH signal if the sound level is above a certain threshold.
Learn how to use the microphone sound sensor to detect sound with the Arduino:
Get a microphone sound sensor.
23. Relay Module
A relay is an electrically operated switch and like any other switch, it that can be turned on or off, letting the current go through or not. It can be controlled with low voltages, like the 5V provided by the Arduino pins, and allows us to control high voltages like 12V, 24V, or mains voltage (230V in Europe and 120V in the US).
Learn how to use a relay module with the Arduino:
Get a relay module:
- 5V 2-channel relay module (with optocoupler)
- 5V 1-channel relay module (with optocoupler)
- 5V 8-channel relay module (with optocoupler)
- 5V 16-channel relay module (with optocoupler)
- 3.3V 1-channel relay module (with optocoupler)
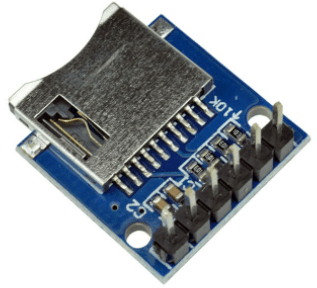
24. microSD Card Module
The microSD card module allows you to interface the Arduino with a microSD card. You can use the microSD card with the Arduino to create, write, read, and delete files. It can be very useful for datalogging, saving configuration files, and other applications.
To get started, follow the next tutorial:
25. Load Cell with HX711 Amplifier
The load cell you see in the picture above is a strain gauge load cell. A strain gauge is an electrical sensor that measures force or strain on an object. The resistance of the strain gauge varies when an external force is applied to an object, which results in a deformation of the object’s shape (in this case, the metal bar). The change of the resistance is proportional to the load applied, which allows us to calculate the weight of objects.
Get started with the following tutorial:
Get a load cell with the HX711 amplifier.
26. Fingerprint Sensor Module (FPM10A)
The fingerprint sensor module, when connected to an Arduino, enables biometric authentication by scanning and recognizing fingerprints.
Get started with the following tutorial:
Get a fingerprint sensor module.
27. TCS230/TCS3200 Color Sensor
The TCS3200 color sensor can detect a wide variety of colors based on their wavelength. This sensor is especially useful for color recognition projects such as color matching, color sorting, test strip reading, and much more.
Learn how to use the TCS3200 color sensor with the Arduino:
Displays
28. OLED Display
The organic light-emitting diode (OLED) display is a monocolor display that doesn’t require backlight, which results in a very nice contrast in dark environments. Additionally, its pixels consume energy only when they are on, so the OLED display consumes less power when compared with other displays. It’s available with different drivers, but we recommend getting the one with the SSD1306 driver, which is the most supported. There is also a wide variety of OLED sizes. We usually use the 0.96-inch display with 128×64 pixels.
Learn how to use the OLED display with the Arduino board:
Get an 0.96inch SSD1306 OLED display.
29. 8×8 Dot Matrix
A dot matrix display when combined with the MAX7219 chip offers a versatile way of showcasing text, graphics, and animations in a visually engaging manner. One very interesting application of the dot matrix is creating a pong game. You can also combine several dot matrixes together to have a larger display area.
Learn how to use the dot matrix with the Arduino and how to create a pong game:
Get a Dot Matrix with the MAX7219 chip.
30. LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)
The simplest and cheapest display screen around is the liquid crystal display (LCD). LCDs are found in everyday electronic devices like vending machines, calculators, parking meters, and printers, and are ideal for displaying text or small icons.
LCDs are measured according to the number of rows and columns of characters that fit on the screen. You’ll find sizes ranging from 8×1 to 40×4. A 16×2 LCD can display 2 rows of 16 characters each and this is the one we use most in our projects.
Get started with with the LCD by creating the following project:
31. 1.8 TFT Display
The 1.8 TFT is a colorful display with 128 x 160 color pixels. The display can load images from an SD card – it has an SD card slot at the back.
Get started with the following tutorial:
32. RGB LED
An RGB LED is a combination of three LEDS (red, green blue) in just one package. You can virtually produce any color by combining those three colors.
Learn how RGB LEDs work and how to control them using the Arduino board:
33. Addressable RGB LED Strip WS2812B
LED strips are just amazing, and there are a wide variety of LED strips to choose from. They can be analog, or digital, and vary in the density and number of LEDs, power supply, etc. To learn more about the main differences between LED strips, I recommend taking a look at the following article: What’s the Best LED Strip For Your Project?
When it comes to digital LED strips, you can control each LED individually – these are also called addressable LED strips. You can choose each LED color, its brightness, and when they should be on and off. This allows you to do all sorts of crazy and awesome effects. Our favorite addressable RGB LED strip is the WS2812B.
Learn how to get started with the RGB addressable LED strip and Arduino
Get a WS2812B addressable RGB LED Strip.
Communication Modules
34. MFRC522 RFID Reader
RFID means radio-frequency identification. RFID uses electromagnetic fields to transfer data over short distances. RFID is useful to identify people, make transactions, open doors, and many other applications.
Learn how to use an RFID reader with the Arduino:
35. nRF24L01
The nRF24L01 modules are wireless communication devices that, when integrated with the Arduino, enable reliable and low-power data transmission between devices over short distances, making them suitable for projects requiring communication between two Arduino boards or between two other microcontrollers.
Get started with the nRF24L01 modules by following the next tutorial:
Get nRF24L01 transceiver modules.
36. 433 MHz Transmitter/Receiver
These RF modules are very popular among the Arduino tinkerers. The 433MHz is used on a wide variety of applications that require wireless control. You can use these modules to establish wireless communication between two Arduino boards or between your board and third-party devices. Learn how to use The 433MHz Transmitter and Receiver with the Arduino:
Get 433 MHz Transmitters and Receivers.
37. Infrared Receiver
The infrared receiver module used with the Arduino allows for the detection and interpretation of infrared signals, enabling projects to receive commands from remote controls or other infrared transmitters. This might be useful for various applications like home automation and remote device control.
Learn how to use the infrared receiver with the Arduino for remote control of devices:
Get an infrared receiver (TSOP4838).
38. SIM900 GSM Shield
The SIM900 GSM shield, when paired with an Arduino, allows you to establish cellular connectivity, allowing projects to send and receive data and messages over the GSM network. This combination is useful for applications such as remote monitoring, SMS notifications, and IoT and home automation projects.
Learn how to use the SIM900 GSM Shield with the Arduino:
- Guide to SIM900 GSM GPRS Shield with Arduino
- Request Sensor Data via SMS using Arduino and SIM900 GSM Shield
Get a SIM900 GSM Shield for the Arduino.
39. Membrane Keypad
A membrane keypad allows you to have a physical interface to interact with your microcontroller. They come in a wide variety of shapes and sizes. The most common sizes are 3×4 and 4×4 and you can get keypads with words, letters, and numbers written on the keys.
Learn how to use the membrane keypad with the Arduino:
Wrapping Up
This was our compilation of tutorials for the most popular sensors, modules, and peripherals compatible with the Arduino boards.
If you have a sensor/module that you would like to be covered on our website, just write a comment below.
We hope you find this article useful. Don’t forget to bookmark this page for the future and share it with a friend that also likes electronics.
We also have a similar compilation article for the ESP32 and ESP8266 boards:
- ESP32: 25 Free Guides for Sensors and Modules
- ESP8266 NodeMCU: 20 Free Guides for Sensors and Modules
earn more about the Arduino with our resources:
Thanks for reading,